
The decision to install residential solar power panels is not a simple one. The question is whether the energy savings will outweigh the costs. You might be wondering if you need a new roof first, or how long solar panels would endure. Before purchasing residential solar panels, there are several variables to consider. We’ll go over the fundamentals of solar panels and address all of your burning questions so you can make the best decision for your house, budget, and energy needs.
What Exactly Is Solar Power?
Simply, solar energy is the most plentiful energy source on the planet. At any given moment, over 173,000 terawatts of solar energy impact the Earth, which is more than 10,000 times the world’s entire energy demands[1].
Capturing the sun’s energy with a commercial or residential solar system that generates clean power is an important answer for tackling the present climate catastrophe and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
How Does Solar Energy Work?

Our sun functions as a natural nuclear reactor. It emits photons, which are small packets of energy that travel 93 million miles from the sun to Earth in roughly 8.5 minutes. Every hour, enough photons collide with our globe to create enough solar energy to meet the world’s energy demands for a whole year.
Currently, solar electricity accounts for just 5% of total energy consumption in the United States. However, as solar technology advances and the cost of going solar falls dramatically, our capacity to capture the sun’s abundant energy grows.
Solar became the world’s fastest-growing source of electricity in 2017, according to the International Energy Agency, marking the first time that solar energy’s growth had overtaken that of all other sources. Since then, solar has continued to expand and shatter records all across the world.
What Effect Does Weather Have on Solar Energy?
Weather conditions may affect the quantity of power produced by a solar system, but not in the way you might imagine.
Of course, ideal conditions for creating solar energy involve a clear, bright day. However, solar panels, like other electronics, are more efficient in cold weather than in warm weather. As a result, the panel may generate more power in the same period of time. The panel creates less voltage and produces less power as the temperature rises.
Despite the fact that solar panels are more efficient in cold weather, they do not always produce more power in the winter than in the summer. Sunnier weather is more common during the warmer summer months. In addition to fewer clouds, the sun is frequently visible for a longer period of the day. Even though solar panels are less efficient in hot weather, they will most likely produce more power in the summer than in the winter.
How Do Solar Panels Works?
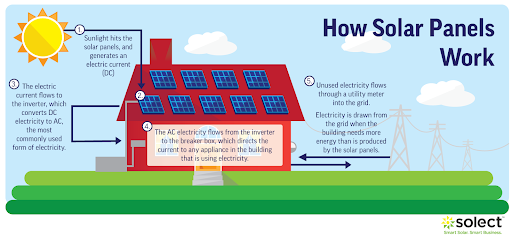
When photons strike a solar cell, they release electrons from their atoms. An electrical circuit is formed when conductors are connected to the positive and negative sides of a cell. When electrons move via such a circuit, electricity is produced. A solar panel is made up of several cells, and many panels (modules) can be linked together to form a solar array. The more panels you can install, the more electricity you can create.
What Materials Are Used in Solar Panels?
PV solar panels are made up of many solar cells. Solar cells, like semiconductors, are constructed of silicon. They are made up of a positive and a negative layer that work together to form an electric field, much like a battery.
The advantages of solar panels
Why would you want solar panels for your home? Solar panels for your house provide several advantages:
- Energy savings: The most obvious benefit is the ability to power your own house independently of the electrical grid. This will save you money, and if you create additional power, you may be able to earn a credit on your energy bill from the company.
- Solar is a plentiful power source: according to the USA News Department of Energy, one hour of summer noontime sun satisfies the whole annual US electricity consumption. Even if you live in a location with a lot of rain or shadow, you may still save money on your power bill.
- Help with house value: If you want to sell your home in the future, installing home solar panels may be a significant benefit to purchasers and can help improve the value of your property.
- Greening up: Because solar is a renewable resource, you can reduce your carbon impact.
- Independence from electrical grid failures: Some places have less-than-reliable electricity grids. If your neighborhood has regular power outages, your own solar electricity can keep the lights on.
- Power your camping: Some tiny solar panel arrays may be attached to RVs or taken camping to provide energy no matter how remote the area.[2]
What Does a Solar Inverter Do?
A solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) power generated by the solar array into alternating current (AC). Inverters act as the system’s brains. They provide ground fault protection and system metrics, including voltage and current on AC and DC circuits, energy output, and maximum power point tracking, in addition to inverting DC to AC power.
Since the inception of the solar business, central inverters have dominated. One of the most significant technological developments in the PV sector has been the advent of micro-inverters. Micro-inverters, unlike central inverters, optimize for each individual solar panel rather than the complete solar system.
This allows each solar inverter to work to its full capacity. When a central inverter is employed, a problem with one solar panel (maybe it is in the shadow or has become dirty) might degrade the overall performance of the solar array. Micro-inverters, such as those used in the home solar system, eliminate this problem. Even if one solar panel fails, the rest of the solar array continues to operate efficiently.
What Is the Role of a Solar Panel System?
Here’s an illustration of how a residential solar energy installation works. First, sunlight strikes a rooftop solar panel. The panels convert the energy into direct current, which is then sent to an inverter. The inverter transforms the electricity from direct current to alternating current, which you may then utilize to power your house. It’s elegantly simple and clean, and it’s becoming more efficient and cost-effective all the time.
But what if you’re not home to consume the power your solar panels produce every sunny day? And what happens at night when your solar system isn’t producing electricity in real-time? Don’t worry, you could still profit from a scheme known as “net metering[3].”
During peak daylight hours, a typical grid-connected PV system usually produces more energy than one client needs, therefore the extra energy is released back into the grid for use elsewhere. Net metering customers may obtain credits for surplus energy produced and utilize those credits to draw from the grid at night or on overcast days. A net meter compares the energy delivered to the grid to the energy received. Read about net metering and how it works in our article.
How Do Solar Panels Produce Energy?
Direct current (DC) power is generated by PV solar panels. Electrons move in one direction around a circuit with DC electricity. In this example, a battery is used to power a light bulb. Electrons travel from the negative side of the battery to the positive side of the battery through the light.
Electrons are pushed and pulled by alternating current electricity, occasionally reversing direction, much like the cylinder of an automobile engine. When a coil of wire is spun adjacent to a magnet, it generates alternating current (AC). This generator may be powered by a variety of energy sources, including gas or diesel fuel, hydroelectricity, nuclear, coal, wind, or solar.
AC energy was selected for the United States’ electrical power infrastructure because it is less costly to deliver across large distances. Solar panels, on the other hand, generate direct current power. How can we get DC power into the AC grid? We make use of an inverter.
How to choose your solar panels in 3 steps?
- Determine the efficiency of solar panels and compare it to the industry average of 16-18%.
- Compare the warranties provided by solar panel manufacturers to the industry average of 10-25 years.
- Cost should be weighed against relative efficiency; efficiency is crucial, but the most efficient panels aren’t necessarily the greatest value.
What factors should I consider before purchasing a solar panel?
Solar panels may be evaluated using three key criteria: production, durability, and manufacturer quality.
The quantity of energy produced by a specific solar panel is determined by various parameters, including the power rating, power tolerance, efficiency, and temperature coefficient. These elements, when combined, will tell you how much electricity your panel can produce.
You should also search for signs of panel maker quality. Begin with the manufacturer’s warranties and promises on their equipment. Solar panels, like all things, deteriorate and become less efficient over time. Many manufacturers will guarantee that the power output of their panels will not fall below a set level for the next twenty-five years.
More ASPECTS
Most solar panels are quite durable, but if you live in a location prone to heavy snow or high winds, you need also to ensure that the panels you install are built to endure the weather. Look for panels that fulfill the International Electrotechnical Commission’s IEC 61215 dependability standard (IEC). To assure the durability of panels, IEC 61215 employs an accelerated outdoor stress test.
While some homes may prefer to invest in the finest quality, most efficient “premium” panels, keep in mind that they will be more expensive. Going solar is like to purchasing a car: not everyone requires a Porsche! In contrast, if you wish to save money by purchasing inexpensive solar panels, your system may produce less power.
Which inverter should I Choose?
The inverter in your solar energy system’s function is to transform solar energy into something usable. Solar panels convert solar energy into direct current (DC) power. The inverter’s duty is to transform the direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity that may be utilised in your house.
Inverters are classified into two types: string inverters and module-level power electronics (MLPEs). MLPEs include both microinverters and power optimizers.
TWO Classification
1- String inverters are the most affordable solar energy system choice. They are typically a fantastic alternative for your house if your system has ideal production conditions. When you have a string inverter on your solar panel system, all of your panels feed all of the DC electricity they create to a single inverter. After the inverter converts the DC energy to AC electricity, your solar energy is ready to use.
2- In general, MLPEs are more costly, but they can also be more efficient. If your solar energy system will be partially shadow or cannot be position at the optimal angle, MLPEs are a suitable option. When you utilize microinverters, each panel has its own inverter that converts the power it generates and feeds it into your home. Power optimizers, like microinverters, are mount on each panel, but they are couple with a string inverter. The energy is “condition” by the power optimizer, making it easier to convert from DC to AC and then to the main inverter.
HOW TO FIND A SOLAR INSTALLATION PARTNER
You’ll probably have a lot of questions when you start looking for solar contractors to assist with your home solar installation. Before you get in and deal with just any old solar installation, properly evaluate each company that you could engage with. You’ll want to select a firm that is eager to work with you and has your best interests in mind. Here are some filters to apply and questions to inquire about.
- How long since they’ve been in operation? Consider five years as a decent starting point.
- Is their website clean and simple to use? A competent business will invest time in its internet presence.
- Do they provide a warranty? Not all businesses will provide craftsmanship guarantees. A solid guarantee is essential.
- Do they provide competent customer service? How you are handle during the sales process is likely to be how you are treat throughout your time working with them.
- Will they be available to you in the future? Finding a firm that is prepare to collaborate with you in the long run, rather than just now, is a major advantage.
Solar panel maintenance and durability
I guarantee many solar panels and solar inverter to last 20 to 30 years, with 25 years being the most typical estimate. They are low-maintenance, needing only that you maintain them clear of debris such as dirt, leaves, and snow. Warranties can also assist with expert repairs.
I measured the usable life of solar panels in years. The panels eventually generate less energy as they age. Around 25 years after installation, you may notice a considerable decrease in the amount of energy you receive from the panels. Many warranties, for example, guarantee 90% of panel output for the first 10 years and 80% for the next 25-30 years[4]. But it doesn’t imply they’re worthless right away; they may still generate energy for a long time.
References
[1] Michelle Honeyager, (4 Nov, 2021),Solar panel buying guide: Everything you need to know[https://www.cnet.com/home/energy-and-utilities/solar-panel-buying-guide-everything-you-need-to-know/]
[2] Energy Sage, 2022, How do I choose my solar panels?[https://www.energysage.com/solar/how-to-go-solar/choosing-solar-equipment/]
[3] Lavancha,2021, A Brief Guide to choosing the right Solar Panel[https://www.lavancha.in/solar-panel-selection-guide/]



